
There are already well over three million industrial robots installed worldwide, and the pace of installation is increasing rapidly. Use cases are proliferating from shelf stacking to cleaning to manufacturing.
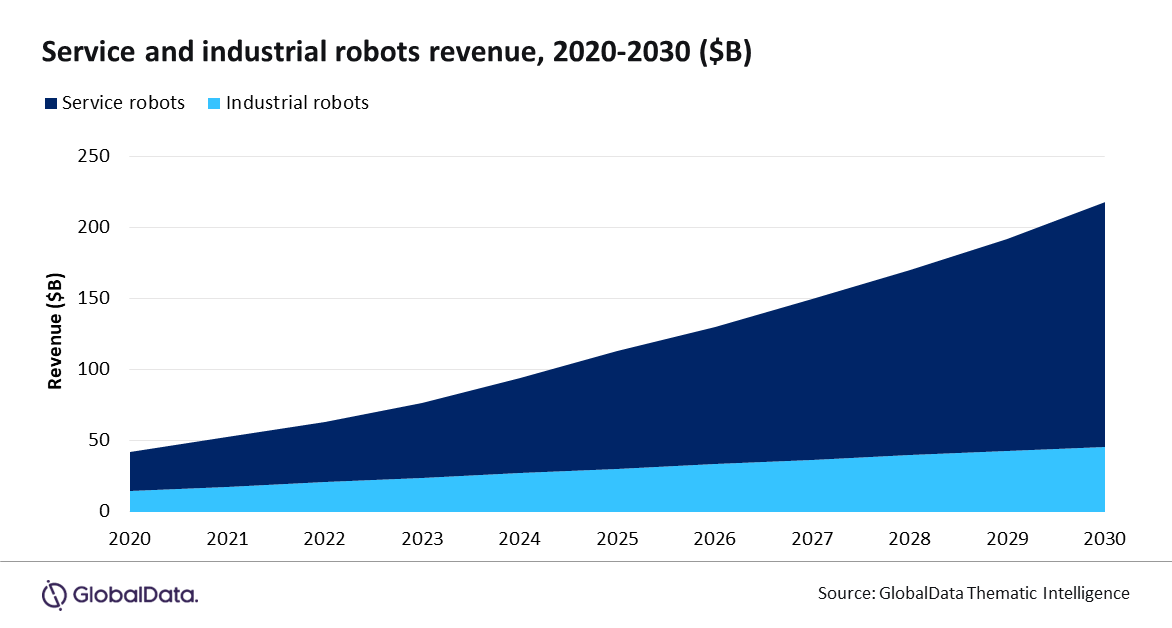
Robots are increasingly important as many countries struggle with labor shortages and aging populations. Against this backdrop, the robotics market is forecast to reach $218 billion by 2030, according to GlobalData.
GlobalData’s latest report, ‘Robotics’, highlights numerous sectors that will be impacted by robots, including industrial, medical, logistics, manufacturing, inspection, cleaning, agriculture, defence and security, and consumer. As robotic intelligence becomes increasingly sophisticated, autonomous machines will become increasingly prevalent in the home and the workplace.
Isabel Al-Dhahir, Senior Analyst, Thematic Intelligence team at GlobalData, comments: “Within healthcare, an increasing number of surgeries are being carried out or assisted by robots. Robots in warehouses and distribution centers are enabling high-efficiency logistics. And on the consumer side, autonomous vacuum cleaners have become commonplace in many households.”
Al-Dhahir continues: “Advances in AI have enabled the development of robots, allowing them to become highly complex products rather than the stand-alone, fixed-function machines they used to be. This, in turn, has increased the number of roles that robots can perform. Cloud computing is central to this development to enable sensing, computation, and memory to be managed more rapidly, securely, and at scale.”
In addition to technological progress, the adoption of robots is strongly tied to current developments. The Russia-Ukraine war has increased the sales of military drones and accelerated their functionalization. Aging populations and low fertility rates in South Korea, Singapore, and Japan have incentivized the use of robots to meet gaps in the labor market. Tech wars between China and the US are also driving the robotics market as efficient, low-cost, and high-quality manufacturing becomes increasingly important.
Al-Dhahir concludes: “Robotics is impacting work by changing production lines and, in some cases, replacing human workers. Robot technologies such as co-bots and logistics robots are coming together to turn factories into advanced engineering labs where assembly line processes and components are constantly analyzed, streamlined, and improved. “Unions, policymakers, and social scientists are increasingly concerned that automation will lead to high levels of unemployment, particularly if the economy cannot create higher-value jobs for those workers that robots will replace.”






