
Teledyne FLIR Defense has released a whitepaper with findings revealing a multi-layered approach, incorporating common architectures and information sharing, among other imperatives, is needed to address the threat to life and property posed by weaponized use of small Unmanned Aerial Systems (sUAS).
In January, non-state actors from Yemen utilized small unmanned aerial systems to launch deadly attacks in the United Arab Emirates that destroyed three refueling vehicles and damaged Abu Dhabi’s international airport. Other drone incidents in the Persian Gulf region include a 2019 strike on the world’s largest oil processing facility in Saudi Arabia.
The whitepaper, The Big Problem with Small Drones (and How to Address It), examines how governments worldwide face a growing need for flexible, tailorable, and affordable Counter-sUAS (C-sUAS) solutions. It looks at current C-sUAS strategy, identifies key challenges, and outlines the critical capabilities governments should consider.
“There’s no ‘silver bullet’ when it comes to countering the huge risks presented by weaponized drones in the hands of bad actors,” said Dr. David Cullin, vice president and general manager of Unmanned and Integrated Solutions at Teledyne FLIR Defense. “What we’ve learned is that governments must address a host of challenges in concert to optimize their defense readiness in the face of UAS attacks.
“Nations around the globe are spending millions of dollars on commercially built counter-drone solutions to address the immediate risks posed by these threats. But they need to approach the problem smartly, both from a technology and cost perspective. Our new whitepaper offers a number of insights from our team of experts,” Cullin adds.
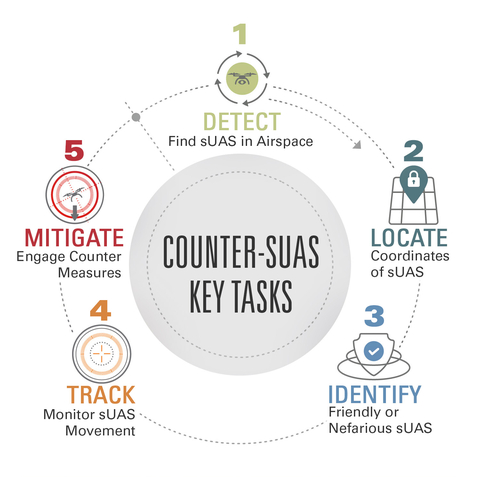
Key findings include:
- State and non-state actors are increasingly employing military- and consumer-grade drones to attack personnel, facilities and critical infrastructure
- Counter-drone solutions must be cost effective, leveraging existing technologies through common electronic architectures and standard interfaces to ensure rapid integration of hardware and software upgrades
- Solutions must be modular, interoperable and multi-domain; easily transportable; and capable of detecting drone swarms
- Modern C-sUAS must be able to operate in contested environments where the ability to find, track, target, engage and assess threats can be disrupted by peer adversaries’ electronic warfare capabilities
- Current and future C-sUAS systems must be flexible in employing both hard kill (kinetic) and soft kill (non-kinetic) countermeasures, allowing them to operate anywhere in the world in accordance with local restrictions and rules of engagement.
As the paper sums up, ‘The threat of small drones in the wrong hands promises to remain significant for government and military decision-makers as they seek to defend forward-deployed units, airports, power grids, and other critical infrastructure. Only the deployment of mature, flexible, and cost-effective C-sUAS solutions will provide the required levels in protection as this threat continues to evolve at pace.”
You can read the full report here.






